//intToBinary.cpp
//HYQ
//Mar 20,2013
const char* bits(unsigned int val){
int i;
unsigned int m;
char* v = new char[(sizeof(val)*8)+1];
int c=48;//ascII char '0'
for(i=0,m=1<<(sizeof(val)*8-1);
m;//until 0
v[i]=(c+!!(val&m)),m=m>>1,i++);
v[i]=0;
return v;
}
Wednesday, 20 March 2013
Int to Binary String
Wednesday, 13 March 2013
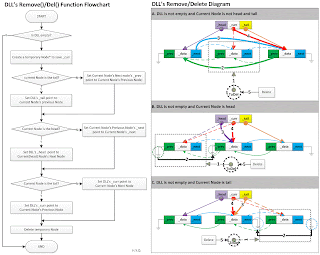
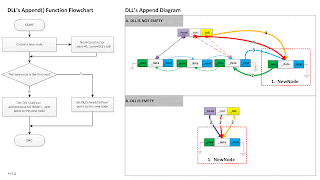
DLL Program
Program of DLL
Function description:
1.DLL constructor
2.DLL destructor
3.DLL Copy constructor
4.DLL operator=()
5.DLL copy()
6.DLL append()
7.DLL insert()
8.DLL remove()
8.DLL del()
Function description:
1.DLL constructor
2.DLL destructor
3.DLL Copy constructor
4.DLL operator=()
5.DLL copy()
6.DLL append()
7.DLL insert()
8.DLL remove()
8.DLL del()
//dll.cpp
//HYQ
//Mar 14, 2013
//Release v0.3
DLL::DLL(){
_head = _tail = _curr = 0;
}
DLL::~DLL(){
while (del());
}
DLL::DLL(DLL& D){//prevent copying
_head = _tail = _curr = 0;
copy(D);
}
DLL& DLL::operator=(DLL& D){
while (del());
copy(D);
return *this;
}
void DLL::copy(DLL& D){
int currPos;
for(currPos=0;D.goPrev();currPos++); // findout where is current
if (!D.isEmpty()) {
for(this->append(D.visit());D.goNext();this->append(D.visit()));
}
for(D.goHead(),this->goHead();currPos;D.goNext(),this->goNext(), currPos--); // set current to what it was before
}
void DLL::append(int data){// add after tail
Node* newNode = new Node(data, _tail);
if (_tail!=0){
_tail = _curr = _curr->_next = newNode;
}
else{
_head = _tail = _curr = newNode;
}
}
void DLL::insert(int data){// inserts data before current
Node* newNode = new Node(data,_curr->_prev,_curr);
if (!isEmpty()){
if (_curr->_prev){
_curr = _curr->_prev = _curr->_prev->_next = newNode;
}
else{
_head = _curr = _curr->_prev = newNode;
}
}
else{
_head = _tail = _curr = newNode;
}
}
int DLL::remove(){// remove the currect goes next if possible
int data = visit();
del();
return data;
}
bool DLL::del(){
bool ok;
if (ok = !isEmpty()){
Node* ToDel = _curr;
if (_curr->_next){//NextNode exists, current node is not tail
_curr->_next->_prev = _curr->_prev;
}
else{
_tail = _tail->_prev;
}
if (_curr->_prev){//current node is not head
_curr->_prev->_next = _curr->_next;
}
else{
_head = _head->_next;
}
if(_curr->_next){
_curr = _curr->_next;
}
else{
_curr = _curr->_prev;
}
delete ToDel;
}
return ok;
}
Tuesday, 12 March 2013
Monday, 11 March 2013
Saturday, 9 March 2013
Program of Queue - get a node's value,previous node,print a queue
Program of Queue
Function description:
1.get a node's value
2.print a queue
3.Find previous node
Function description:
1.get a node's value
2.print a queue
3.Find previous node
//queue.cpp
//H.Y.Q
//Mar 08, 2013
//Release v0.2
//Get the data's value of current Node
int Queue::get(const Node* currentNode) const {
return currentNode->_data;
}
//Print the Node's data value in the queue
void Queue::print(){
Node* toPrint = _head;
int i=0;
while ((toPrint !=0) &&
(cout << (++i)<< ". Data: "<< get(toPrint) << "\tAddress: " << (void*) toPrint << endl) &&
(toPrint = nextNode(toPrint)));
}
//Return the previous Node of current Node
Node* Queue::prevNode(const Node* currentNode) const{
Node* prev = _head;
while (prev != 0 && nextNode(prev) != currentNode){
prev = nextNode(prev);
}
return prev;
}
Program of Queue - add and remove node,next node in the queue...
Program of Queue
Function description:
1.Add a node
2.Remove a node
3.Find next node
Function description:
1.Add a node
2.Remove a node
3.Find next node
//queue.cpp
//HYQ
//Mar 07, 2013
//Release v0.1
#include "queue.h"
using namespace std;
Node::Node(int data, Node* next){
_data = data;
_next = next;
}
Queue::Queue(){
_head = (Node*)0;
}
//add a Node at the end of queue
void Queue::add(int data){
Node* toAdd=_head;
Node* add = new Node(data);
if (_head){
while ((nextNode(toAdd)!=0) && (toAdd=nextNode(toAdd)));
toAdd->_next = add;
}
else{
_head = add;
}
}
int Queue::remove(){
int ret = _head->_data; // 1
Node* toDel = _head; // 2
_head = _head->_next; // 3
delete toDel; // 5
return ret;
}
bool Queue::isEmpty(){
return !_head;
}
//Return the next Node of current Node
Node* Queue::nextNode(const Node* currentNode) const{
return currentNode->_next;
}
Queue::~Queue(){
while(!isEmpty()){
remove();
}
}
Saturday, 2 February 2013
A simple way to insert a char into a string
This following code is used to insert a char into *str without declaring any temporary string variable:
Shift each char in the *str from last char to the current position to the one right position(move the '\0' first untill the current postion)
Hope you can get inspiration from this segment:
Please leave your comment if any problems.
Shift each char in the *str from last char to the current position to the one right position(move the '\0' first untill the current postion)
Hope you can get inspiration from this segment:
int i; int lcstrPos; //Cursor Position in the string int strLength; strLength = strlen(str); lcstrPos = *curPosition + *strOffset; for(i=strLength+1;i>lcstrPos;str[i--]=str[strLength--]); str[lcstrPos] = key;
Please leave your comment if any problems.
Monday, 21 January 2013
OOP344 exercise -Week2
1. write 4 command line programs to do
$ add num num<ENTER>
$ sub num num<ENTER>
$ mul num num<ENTER>
$ div num num<ENTER>
// command.cpp
//calculate.cpp
2. write a program to show the content of an Operating system environment variable
$ pnenvr path
The output will be either the "content" of path variable or "not found" if the environment variable does not exist.
$ add num num<ENTER>
$ sub num num<ENTER>
$ mul num num<ENTER>
$ div num num<ENTER>
// command.cpp
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
char comm[100]="calculate";
int i;
if(argc < 3)
{
cout <<"ERROR: Please enter the command followed by two numeric at least...\n" << endl;
return 1;
}
for (i = 0; i < argc; argv++, i++){
strcat(comm, " ");
strcat(comm,*argv);
}
system(comm);
return 0;
}
// after compile command.cpp, copy "command.exe" file to "add.exe, sub.exe, mul.exe,div.exe"; or alias command in the Linux bash shell.
//calculate.cpp
#include "ctype.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void cal(int argn,char* argvc[]);
void results(double);
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
if (argc > 3)
cal(argc,argv);
else
cout << "ERROR: Invaild Command."<<endl;
return 0;
}
void cal(int argn,char* argvc[]){
double re = 0;
int i;
if ( strcmp(*(argvc+1),"add")==0){
for( i = 2; i < argn ; i++){
if (i > 2) cout << " + ";
if (i > 0) cout << argvc[i];
re += atoi(argvc[i]);
}
}
else if ( strcmp(*(argvc+1),"sub")==0){
re = (atoi(argvc[2])*2);
for( i = 2; i < argn ; i++){
if (i > 2) cout << " - ";
if (i > 0) cout << argvc[i];
re -= atoi(argvc[i]);
}
}
else if ( strcmp(*(argvc+1),"mul")==0){
re = 1;
for( i = 2; i < argn ; i++){
if (i > 2) cout << " * ";
if (i > 0) cout << argvc[i];
re *= atoi(argvc[i]);
}
}
else if ( strcmp(*(argvc+1),"div")==0){
re = atoi(argvc[2]);
re *= re;
for( i = 2; i < argn ; i++){
if (i > 2) cout << " / ";
if (i > 0) cout << argvc[i];
re /= atoi(argvc[i]);
}
}
results(re);
}
void results(double re){
cout << " = " << re << endl;
}
2. write a program to show the content of an Operating system environment variable
$ pnenvr path
The output will be either the "content" of path variable or "not found" if the environment variable does not exist.
//Show the content of an Os environment variable
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[], char* env[]){
int i;
string s1(argv[1]);
string s2;
string token("=");
bool find=false;
s1.append(token);
transform(s1.begin(), s1.end(), s1.begin(), ::toupper);
for(i=0;env[i] != 0;i++){
s2=env[i];
transform(s2.begin(), s2.end(), s2.begin(), ::toupper);
s2=s2.substr(0,s1.length());
if (s2 == s1) {
find=true;
cout << env[i] << endl;
break;
}
}
if (find != true)
cout << "Not found" ;
return 0;
}
Monday, 14 January 2013
Walkthrough-2
The output of the program is:
void main()
{
char s[20];
char* p = "string";
int i;
int len = strlen(p);
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
s[i] = p[len-i];
printf("%s".s);
}
A. string B. gnirt C. gnirts D. No output is printed
Answer is D.
void main()
{
char s[20];
char* p = "string";
int i;
int len = strlen(p);
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
s[i] = p[len-i];
printf("%s".s);
}
A. string B. gnirt C. gnirts D. No output is printed
Answer is D.
Friday, 11 January 2013
C++ FAQs
Q1: What is OOPS?
A1: Object-Oriented Programming Systems is a programming paradigm using "objects". Objects are data structures consisting of data fields and methods together with their interactions. Programming techniques may include features such as data abstraction, encapsulation, messaging, modularity, polymorphism, and inheritance.
Q2:What is the major components of OOP?
A2: (1). Abstraction (2). Encapsulation (3). Polymorphism (4). Inheritance
Q3: "struct" vs "class" in C++.
A3: struct and class are same except that in case of structures, default scope is public, and in case of classes, default scope is private. There is a difference between C-struct and C++-struct, C-structure cannot have function whereas C++-structure can have functions(same as classes).
A1: Object-Oriented Programming Systems is a programming paradigm using "objects". Objects are data structures consisting of data fields and methods together with their interactions. Programming techniques may include features such as data abstraction, encapsulation, messaging, modularity, polymorphism, and inheritance.
Q2:What is the major components of OOP?
A2: (1). Abstraction (2). Encapsulation (3). Polymorphism (4). Inheritance
Q3: "struct" vs "class" in C++.
A3: struct and class are same except that in case of structures, default scope is public, and in case of classes, default scope is private. There is a difference between C-struct and C++-struct, C-structure cannot have function whereas C++-structure can have functions(same as classes).
Thursday, 10 January 2013
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)